Principles
& Best Practices of REST API Design
RESTful API Design the Best Practice
This best-practices article
intends for developers interested in creating RESTful Web services that
provided high reliability and consistency across multiple services suites;
following these guidelines; services are positioned for rapid, widespread,
public adoption by internal and external clients.
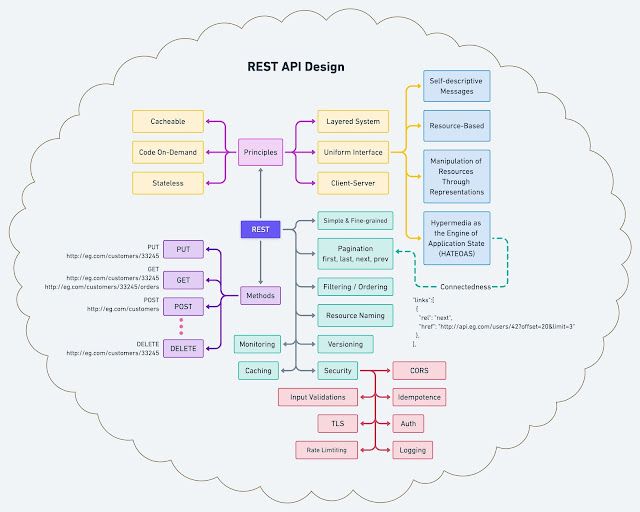
Here is the complete diagram
to easily understand RES API’s principles, methods and best practices.
Now, let’s begin with elaborating on each box by starting
with tis principles.
The Six Principles / Constraints
Client-Server
Separation of concerns is the
principle behind the client-server constraints. By separating the user
interface concerns from the data storage concerns, we improve the portability
of the user interface across multiple platforms and improve scalability by
simplifying the server components.
Stateless
Communication must be
stateless, as in the client-stateless-server (CSS) style. Each request from the
client to server must contain all of the information necessary to understand
the request. Session state is therefore kept entirely on the client.
Cacheable
To improve network efficiency,
we add cache constrains to form the client-cache-stateless-server style. Cache
constraints require that the data respond to a request with the implicit or
explicit label as cacheable or non-cacheable. If a response is cacheable, then
a client cache is given the right to reuse that response data for later,
equivalent request.
Layered System
A client cannot ordinarily
tell whether it is connected directly to the end server or an intermediary
along the way. Intermediary servers may improve system scalability by enabling
load-balancing and by providing shared caches. Layers may also enforce security
policies.
Code-on-Demand
REST allows client
functionality to extend by downloading and executing code in the form of
applets or scripts. Simplifies clients by reducing the number of features
required to be pre-implemented. It allows features to download after deployment
improves system extensibility.
Uniform Interface
By applying the software
engineering principle of generality to the component interface, the overall
system architecture becomes simplified, and the visibility of interactions is
improved. Implementations decouple from the services they provide, which
encourages independent evolvability. REST defines by four interface
constraints: identification of resources, manipulation of resources through
representations, self-descriptive messages, and Hypermedia as the engine of
application state.
Self-descriptive
Messages: Each message includes enough information to describe how
to process the message.
Resource-Based: Individual
resources are identified in request using URLs as resource identifiers. The
resources themselves are conceptually separate from the representation that
returns to the client.
Manipulation
of Resources through Representations: When a client represents a resource, including any metadata
attached, it has enough information to modify or delete the resource on the
server, provided it has permission to do so.
Hypermedia
as the Engine of Application State (HATEOAS): clients deliver state
via body contents, query-string parameters, request headers, and the requested
URL (the resource name). Services provide the state to clients via body
content, response codes, and response headers.
Best Practices
Now, let’s change the gear to
understand REST’s essential best practice, which every engineer should know.
Keep it Simple and Fine-Grained
Create API’s that mimic your
system’s underlying application domain or database architecture of your system.
Eventually, you’ll want aggregate services – services that utilize multiple
underlying resources to reduce chattiness.
Filtering & Ordering
For large data sets, limiting
the amount of data returned is vital from a bandwidth standpoint. Additionally,
we may want to specify the fields or properties of a resource to be included in
the response, thereby limiting the amount of data that comes back. We
eventually want to query for specific values and sort the returned data.
Versioning
There are many ways to break a
contract and negatively impact your clients in API development. If you are
uncertain of the consequences of your changes, it is better to play it safe and
consider versioning. There are several factors to consider when deciding if a
new version is appropriate or if a modification of the existing representation
is sufficient and acceptable. Since maintaining many versions becomes
cumbersome, complex, error-prone, and costly, you should support no more than
two versions for any given resource.
Cache
Caching enhances scalability
by enabling layers in the system to eliminate remote calls to retrieve
requested data. Services improve cache-ability by setting headers on responses
such as Cache-Control, Expires, Pragma,
Last-Modified etc.
Pagination
One of the principles of REST
is connectedness via hypermedia links. At the same time, services are still
helpful without them. APIs become more self-descriptive when links return in
the response. For collections returned in a response that supports Pagination, ‘first’,
‘last’, ‘next’, and ‘prev’ links at a minimum are beneficial.
Resource-Naming
An API is intuitive and easy
to use when resources are named well. Done poorly, that same AI can feel klutzy
and be challenging to use and understand. RESTful APIs are for consumers. The
name and structure of URIs should convey meaning to those consumers. It’s often
difficult to know what the data boundaries should be, but with the
understanding of your data, you must likely are equipped to take a stab and
what makes sense to return as a representation to your clients. Design for your
clients, not for your data.
Pluralization
The commonly-accepted practice
is always to use plurals in node names to keep your API URIs consistent across
all HTTP methods. The reasoning is that `customers` are collection within the
service suite and the ID (e.g., 23223) refers to one of those customers in the
collection.
Monitoring
Make sure to add all kinds of
monitoring to improve the quality or performance of your API. Data points can
be Response Time (P50, P90, P99), Status Codes (5XX, 4XX, etc.), Network
Bandwidth, and many more.
Security
1. Authorization / Authentication:
Authorization for services is no different than authorization for any
application. Ask this question, “Does this principal have the requested
permission on the given resource?”
2. CORS: implementing CORS on a
server is as simple as sending an additional HTTP header in the response, such
as Access-Control-Allow-Origin,
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials, etc.
3. TLS:
all authentications should use SSL. OAuth2 requires the authorization server
and access token credentials to use TLS.
4. Idempotence: an
operation that will produce the same results if executed once or multiple
times. It may have a different meaning depending on the context in which it
applies. In the case of methods or subroutine calls with side effects, for
instance, it means that the modified state remains the same after the first
call.
5. Input Validation:
Validate all input on the server. Accept “known” good input and reject bad
input, Protect against SQL and NoSQL injection, Restrict the message size to
the exact length of the field, services should only display generic error
messages, and many more.
6. Rate limiting: is a
strategy for limiting network traffic. It puts a cap on how often someone can
repeat an action within a certain timeframe for instance, trying to log into an
account.
7. Logging: Make sure you do not
accidentally log any personally identifiable information (PII).
With that I conclude this
learning; I hope you have learned something new today. Thanks for reading and
have a wonderful learning experience in your adventure in tech.

Comments
Post a Comment